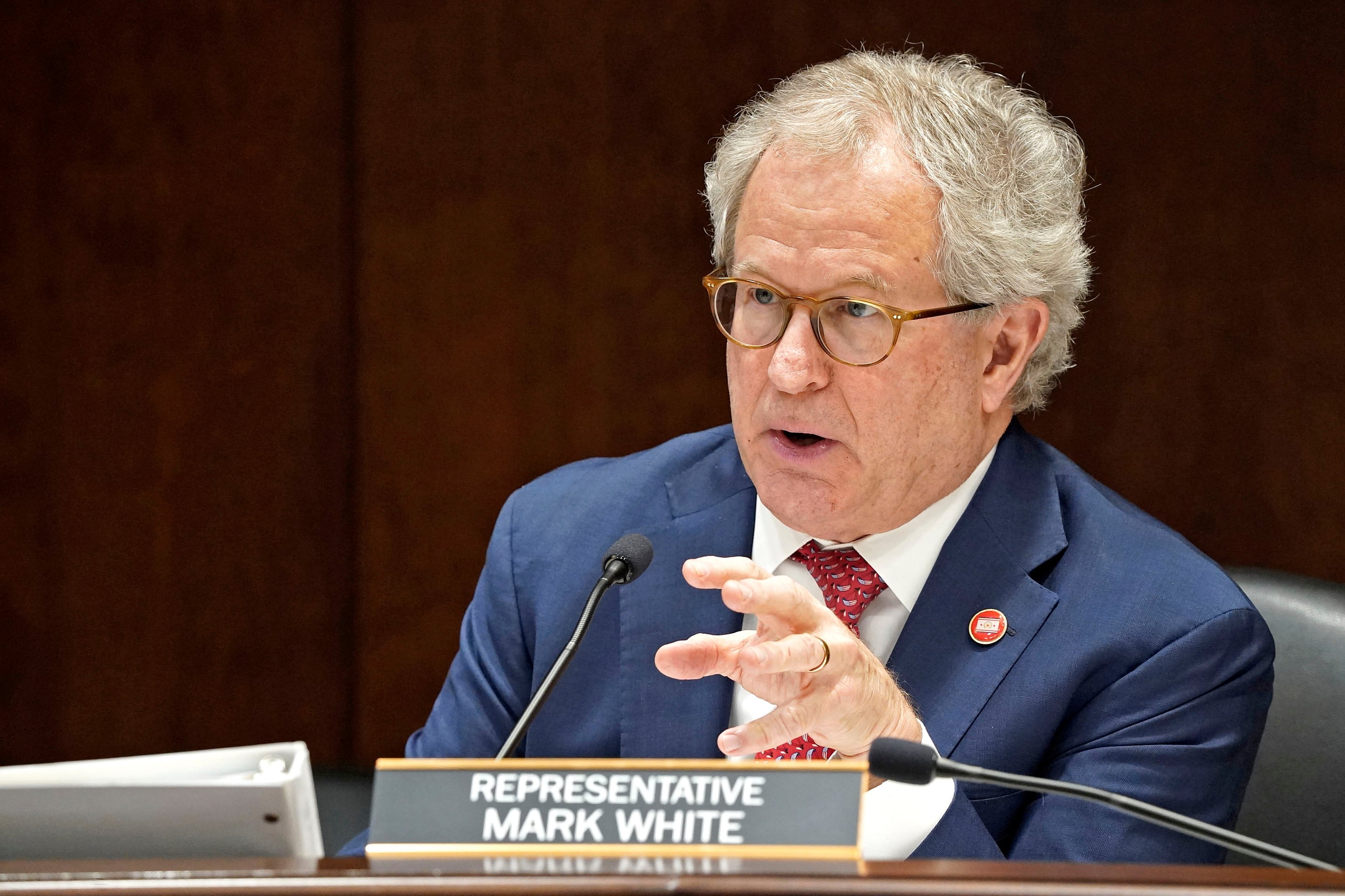
A leading House Republican has filed legislation in Tennessee to widen criteria for determining which third graders are at risk of being held back if they aren’t deemed proficient readers.
A 2021 law pins the entire decision on scores from the state’s annual TCAP test given each spring for English language arts. But a proposal filed Monday by Rep. Mark White would consider results from a second state-approved test, too.
Under White’s legislation, third graders who don’t score as proficient on their TCAP could still avoid retention and related learning interventions if they score in at least the 50th percentile on their most recent reading benchmark test. Districts give those assessments periodically throughout the school year to measure students’ reading skills, fluency, and comprehension.
White is seeking to satisfy educators and parents who are unhappy that the state’s new retention policy hinges on scores from a single state test that could impact tens of thousands of third graders this year. However, his proposal would not give authority back to local educators to make the final decision, as called for by numerous school boards, the state superintendents association, and several teacher groups.
At the outset of this year’s General Assembly, legislative leaders said revisiting the controversial reading and retention law was their No. 1 education priority. Lawmakers have filed a flurry of bills with various ideas.
White’s legislation includes components from several of those bills but carries particular sway, because the Memphis Republican chairs the House Education Administration Committee and also sits on a K-12 subcommittee that is deciding which proposal moves forward. The Senate, where Education Committee Chairman Jon Lundberg is co-sponsoring White’s bill, is letting the House take the lead on vetting any proposed revisions.
After holding a legislative hearing last month on Tennessee’s reading problem, White huddled in recent days with other House GOP leaders to try to reach a consensus on how to address local concerns about the controversial law, which Republican Gov. Bill Lee pushed for as a key part of Tennessee’s pandemic learning recovery plan.
The law also created summer learning camps and tutoring programs to support students who are struggling in reading and math and to provide avenues to avoid retention if they don’t test as proficient readers in the third grade, which is considered a critical marker for learning in subsequent grades.
The K-12 subcommittee, chaired by Republican Rep. Kirk Haston, from Lobelville, is scheduled to discuss the various bills on March 14.
In addition to adding benchmark test results to the retention equation, White’s legislation seeks to make clear that a parent or guardian can appeal a retention decision under certain circumstances, or give written permission for their child’s teacher, guidance counselor, or school administrator to file an appeal.
White also proposes a new requirement that any public school student held back in kindergarten, first grade, or second grade be assigned a tutor and undergo tutoring for the entire next school year.
You can read White’s amendment below.